‘Biomass’ is the mass of living organisms - such as plants, animals, microorganisms, and more – and it serves as a natural reservoir of energy / it is used to generate energy. In this article, we’ll explore what biomass is and how it can help address the world’s energy-related challenges.
―
Q. What is Biomass?
―

A. Bio means “life” and mass is the “quantity of matter in a body.” Therefore, the word biomass refers to the matter from living organisms, which includes plants, animals, and microorganisms, that can be utilized as a natural reservoir of energy to generate a new form of energy.
One great advantage of utilizing biomass as a renewable energy source is that it is much less harmful the environment than other energy sources.
You may be surprised to find that there are buses that run on animal feces / waste. In the city of Linköping in Sweden, you can find these innovative buses running on biogas made from animal waste.
In other words, gas from cow or pig feces is recycled to power buses. Believe it or not, Sweden is saving tons of oil as well as the environment every year by doing so. Biomass has the great advantage of being a sustainable source of energy and less harmful to the environment, and this is one example of why it’s being touted as a major contributor to climate change mitigation.
Are you interested in learning about nature-based solutions? Then check out this article! ↓↓↓ |
―
Why is Biomass Important?
―
1. Biomass is a renewable energy source.
Biomass is a renewable source of energy just like the sun and wind. If managed properly, it can be used infinitely: organic matter from agriculture, industry, and life can be recycled into energy, making efficient use of resources.
2. Biomass can help mitigate climate change.
Replacing fossil fuels with biomass can reduce carbon dioxide emissions. Some of the biomass materials such as trees and plants absorb carbon dioxide as they grow, so using them as fuel will result in lower net carbon dioxide emissions.
Biomass is a heavily researched topic in Nordic countries like Sweden. Based on its carbon neutrality, renewability, and ability to cycle carbon dioxide, it can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by up to 86% when used in place of fossil fuels.
3. Biomass creates jobs.
The biomass industry can create jobs in a variety of sectors, including agriculture, manufacturing, and research and development. In the United States, the biomass industry provides tens of thousands of jobs, reportedly 68,000 jobs in 2016 alone.
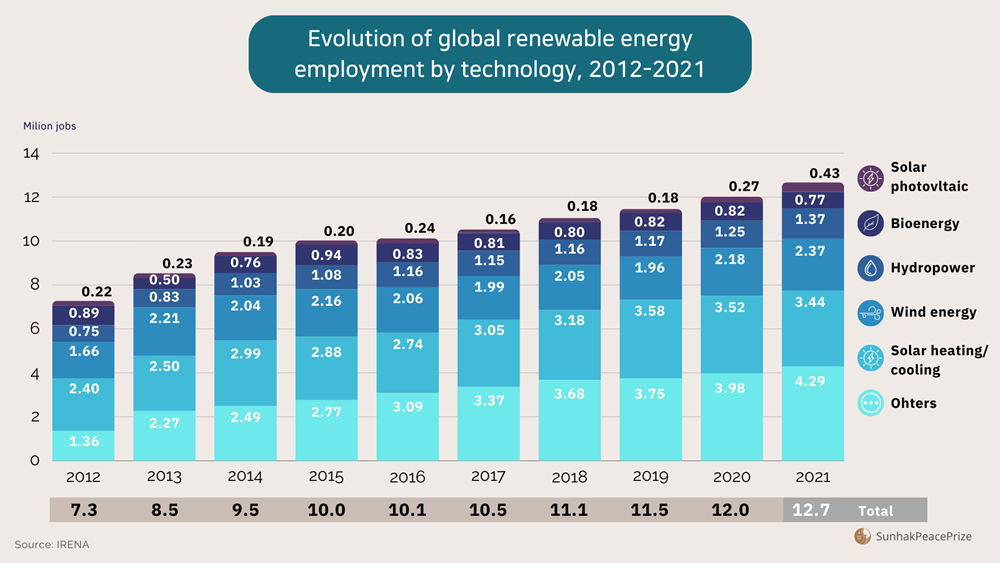
Evolution of global renewable energy employment by technology, 2012-2021 (Source: IRENA)
―
Different Types of Biomass
―
What are the different types of biomass? It comes in a variety of forms such as wood, grain, animal waste, and algae, each with different potentials and uses.
1. Wood and wood waste
· Worldwide, the share of wood in the biomass energy production is about 44%.
· In the United States, more than 200 million tons of wood biomass are produced annually.
2. Grains
· Corn, sugarcane, and wheat are the major grains used as biomass energy. They are mainly used to produce bioethanol, biodiesel, biogas, etc.
3. Animal waste
· Dung from cows, pigs, and sheep is very effective in producing methane gas. On the other hand, the excrement of poultry such as chickens, ducks, and geese contain high nitrogen and is used as fertilizers as well as biogas.
4. Algae
· Oil is extracted from various types of algae such as kelp, chlorella, and spirulina and utilized as biodiesel.
That’s a whole variety of biomass! But actually, there’s even more biomass close to home.
For example, energy can be made from coffee grounds, which can be collected and sent to a power plant to be converted into energy. By doing so, you can address two issue – solve the trash problem and generate energy at the same time. A Danish company called Kaffee Bueno is utilizing this method, using coffee grounds to produce a variety of products and biomass energy.

Source: Kaffee Bueno
―
Global Use of Biomass
―
Biomass accounts for about 10% of the green energy generated worldwide. Let’s find out what that number signifies.
· United States: In the U.S., trees, farm leftovers, animal waste, and more are collected to generate electricity. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), about 16,654 megawatts (MW) of electricity was generated in 2019, accounting for 1.4% of all electricity in the country.
· Europe: In Europe, energy from biomass accounts for 60% of all green energy. Europe’s biomass and biogas power generation capacity was about 130 gigawatts (GW) in 2019, with the Nordic countries of Sweden, Finland, and Denmark being particularly good at utilizing biomass.
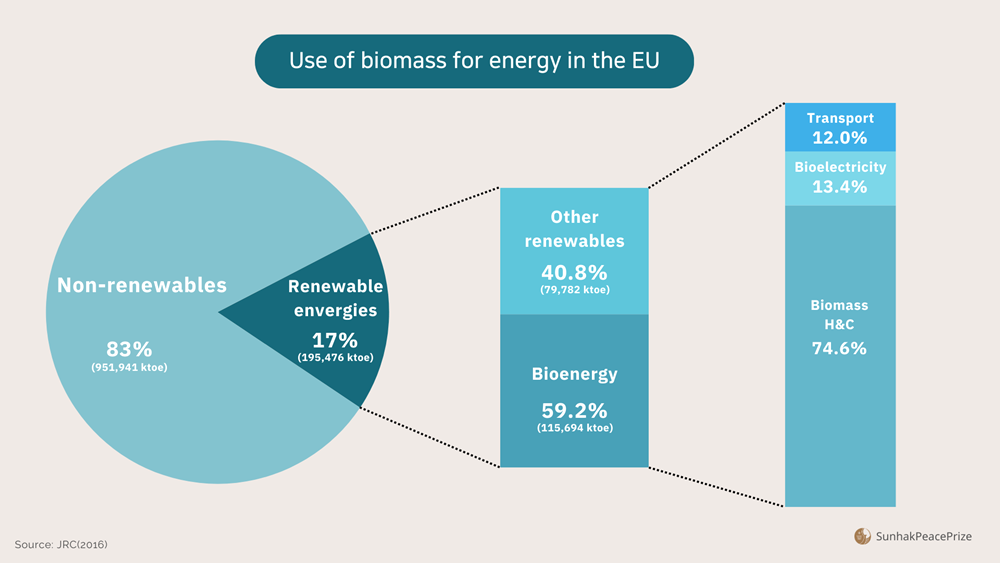
Use of biomass for energy in the EU in 2016 / Source: JRC
· China: China is the largest producer of biomass energy in Asia, generating about 17.5 gigawatts (GW) of energy from biomass in 2020.
· India: India is collecting farm residues to make electricity, and in 2019, they generated about 10 gigawatts (GW) of electricity.
The numbers show that biomass is indeed becoming an important energy source around the world.
―
Biomass Guidelines for Sustainability and the Environment
―
You may think that sustainable biomass is just a matter of making more of it, but that is not the case. Mismanaged biomass can have negative socio-environmental impacts, such as higher food prices, farmland takeover, and biodiversity loss.
The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has a come up with a guideline and policy recommendations regarding biomass.
1. Sustainable Resource Management
The energy consumed and pollutants produced during the production, transportation, and processing of biomass should be properly managed. It means making sure that large-scale agriculture for biomass production does not lead to soil composting and water shortages.
2. Food vs. Fuel
We need to find ways to minimize the impact of biomass utilization on food prices and supply. In the mid-2000s, many countries adopted policies to increase bioenergy. Plants such as corn, sugarcane, and soybeans were heavily used as fuel, driving up food prices, which ultimately led to the 2007-2008 world food price crisis.
3. Protection of Ecosystems
To ensure that local biodiversity is not compromised by the development of new farmland or forestry activities to produce biomass, technologies and mechanisms to utilize resources in a sustainable manner should be developed.
To learn more about biodiversity, check out this article! ↓↓↓ |
―
Towards a Carbon-Neutral Planet with Biomass
―

We hope reading this article helped you to learn about biomass and its role as a source of green energy. It goes beyond mere energy – it’s a powerful tool that can help rescue our planet.
Just picture riding on a bus powered by your coffee grounds or using electricity generated from animal waste. Biomass has the incredible potential to transform everyday items into substantial sources of energy.
At this very moment, extraordinary developments involving biomass are unfolding, and innovators are brainstorming ways to push the boundaries further. And you could be that innovator.
Join the remarkable energy revolution for our planet,
And become part of the movement!
“To embrace the future,
we must expand the scope of vocations that can herald the coming of peace.
Even though we may never meet our descendants, we must make sure that all their activities will harmonize in peaceful societies and nations.”
-Dr. Hak Ja Han Moon
Founder of Sunhak Peace Prize-
Learn More: Find the answer in nature through Nature-based Solutions |
References Evolution of global renewable energy employment by technology, 2012-2021 (Source: IRENA) |
Written by Sharon Choi
Director of Planning
Sunhak Peace Prize Secretariat
Translated by Hyang Oh

