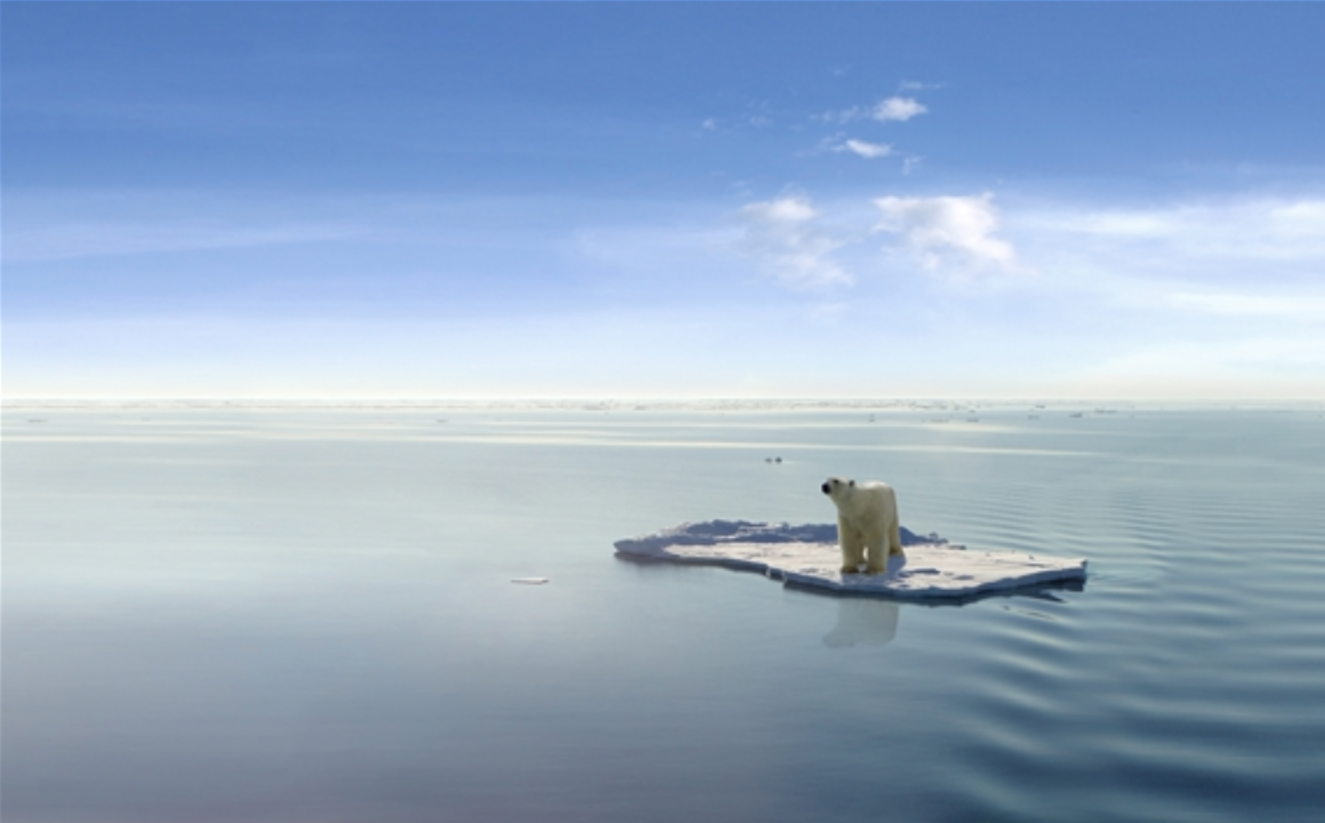
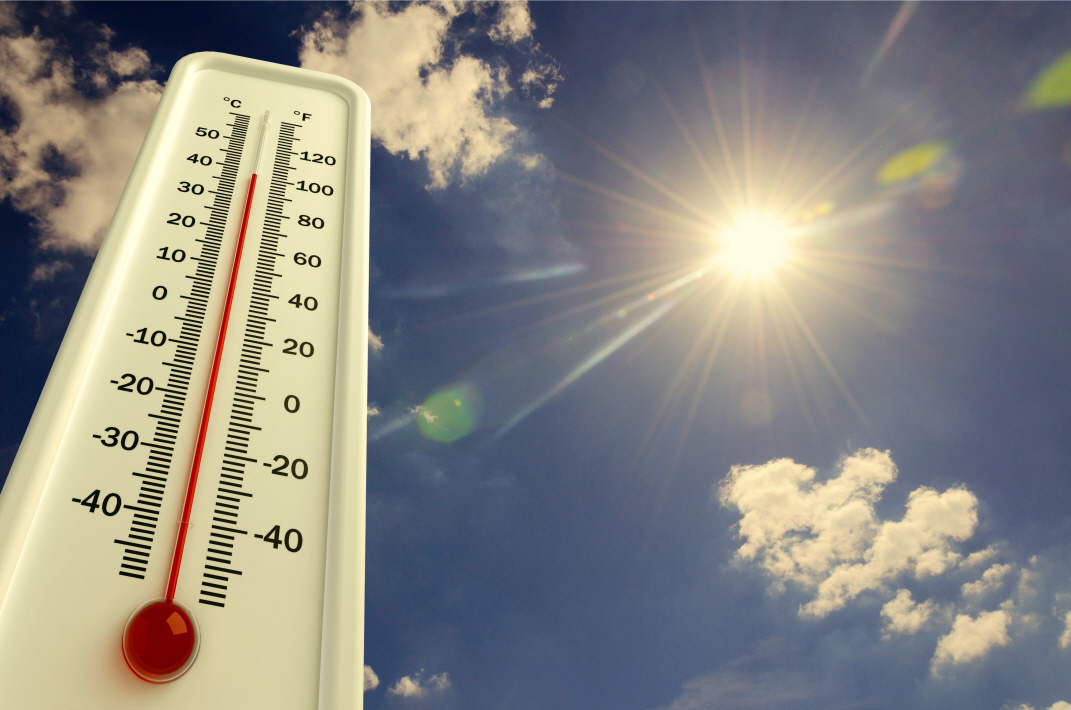
In the summer of 2007, the Arctic sea ice that had remained frozen for thousands of years began to melt. Its surface area decreased to a quarter of what it was before. Due to these changes in the Arctic Ocean ecosystem, many animals, including polar bears, have become endangered.
But is global warming a problem only for polar bears?
ㅡ
The threat we are facing now
ㅡ
For the past 100 years, the Earth has become warmer at a faster pace than ever before. The Earth’s temperature has never changed by more than 1°C in the previous 10,000 years, but in the recent 100 years since the Industrial Revolution, the Earth’s temperature rose by 1°C. This phenomenon of the Earth becoming warmer is called global warming.

Reasons the Earth’s temperature is rising
l Human activity
Climate change can occur due to natural causes but the climate change being experienced in the past 100 years has been accelerated by human activity.
l Greenhouse gases and greenhouse effect
Ninety-nine percent of the Earth’s atmosphere is composed of nitrogen and oxygen. The remaining one percent is mostly made up of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor. These greenhouse gases create the appropriate temperature for us to live in. Over the past 100 years, the concentration of greenhouse gases in the Earth’s atmosphere has increased by more than necessary, which has warmed up the Earth.
Greenhouse gases are accelerating global warming
ㅡ

Reasons greenhouses gases are increasing
l Indiscriminate use of coal and oil
The biggest cause of greenhouse gases is fossil fuels such as coal and oil, which make up more than 90 percent of the energy source used on Earth today. Fossil fuels are used in thermal power plants that produce electricity, factories that mass-produce various products needed in daily life, and transportation methods such as cars and trains. Although the use of fossil fuels has allowed material abundance and convenience for humankind, it is destroying the Earth’s ecosystem.
l Methane emitted by livestock
Methane emitted by livestock raised for human consumption, especially cattle, has 30 times more global warming potential than carbon dioxide. Surprisingly, about 20% of all greenhouse gases are emitted by livestock. This is more than the amount produced by cars.
l Huge increase in garbage
The tremendous amount of garbage being produced since Industrialization is also a factor. A large amount of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, is produced during the process of breaking down the huge amount of garbage that is generated every day.
l Indiscriminate deforestation
Forests around the world, including the Amazon rainforest popularly known as the lungs of Earth, are shrinking significantly due to indiscriminate development. When forests shrink, nature’s ability to absorb greenhouse gases is also reduced, which further speeds up global warming.
ㅡ
Effects of global warming felt in our daily lives
ㅡ
Global warming is transforming not just the climate but the Earth’s ecosystem. As climate changes, ecosystems can be destroyed and can lead to big changes throughout the food chain affecting our lives as well.




l Conservation of energy and resources
If we lower heating by 1°C, 231kg of carbon dioxide can be saved annually per household. Energy can be saved by keeping winter season heating to under 20°C and summer season indoor temperature to between 26~28°C. If we decrease our time in the shower by 1 minute, we can reduce the amount of carbon dioxide produced by 7kg. Installing water-saving showerheads and water-efficient toilets, turning off the faucet while brushing our teeth, and doing laundry after clothes have been collected are all ways of conserving energy that we can practice in our daily lives.
l Use of public transportation and bicycles
We can improve our health and the health of the Earth by taking the bus, subway, and walking. By walking or riding the bicycle, carpooling, and using energy-efficient cars, we can reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
l Use of eco-friendly products
When considering products with the same function, consider using a product that produces less environmental pollution. Select products that are energy-efficient or produce less waste.
l Planting trees
Trees absorb carbon dioxide. A pine tree absorbs 5kg of carbon dioxide per year. Northern Europe, which is heavily forested, has a greater absorption level of carbon dioxide and faceless pressure of reducing greenhouse gases. Efforts should be made to conserve forests and plant new trees.
The climate environment is an international public good that all nations on Earth enjoy together. Therefore, it is impossible to make one nation or individual take responsibility for climate change. Developed nations that have already industrialized need to take lead and support the climate change response of developing nations to reduce the gap among nations. Policy development and implementation on a national level and individual effort in daily lives are also important.
ㅡ
Our house is on fire!
The time to act is now
ㅡ
-
PREV No previous post.
-
NEXT We need to create a better world where we live together with refugees

