As the crisis of climate warming
escalates, the electric vehicles are also proliferating. By 2025, the
global EV supply is expected to reach 20.6 million—more than three times
the number in 2021.
On June 1, Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF), an
energy research institute, published the “2022 Electric Vehicle Forecast Report.”
The report predicts that the global supply of EVs will increase from 6.6
million units in 2021 to 20.6 million vehicles by 2025.
In addition, the BNEF predicts that by 2025,
Europe and China will account for 80% of global EV sales, and the
proportion of EVs in Germany, the UK and France could also rise to 40-50%.
https://about.bnef.com/electric-vehicle-outlook/
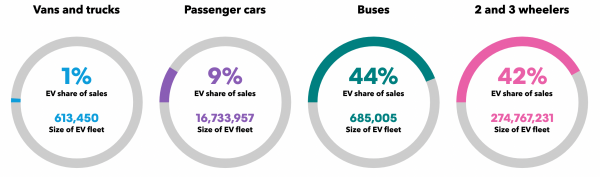
Electric Vehicle Sales by Vehicle Type as of 2021 (BNEF)
The growth rate of electric vehicles is now very steep.
Currently,
electric vehicles are reducing oil demand by 1.5 million barrels per day, and this amount is said to increase to 2.5 million
barrels per day by 2025.
In fact, sales of internal combustion
automobiles peaked in 2017 and are in steady decline, and this downward
trend is expected to continue in proportion to the increase in the number of
electric vehicles.
Norway ranks first in
the world for EV penetration. In Norway, 90% of new vehicles are already
electric (including hybrids). Moreover, Norway has
announced that it will sell fossil fuel burning automobiles only until 2025,
after which it will stop selling.
Electric vehicle penetration in China is also very
steep. The penetration rate of electric vehicles in the PRC this year is
20%, a tenfold increase compared to five years ago. There is also news that
Beijing has decided to allocate 70% of license plates for new cars only to
electric and hybrid vehicles.
China has already decided to provide subsidies for
the purchase of electric vehicles only till the end of this year, as the demand
for EVs has surpassed that for internal combustion vehicles.
―
Electric vehicles are eco-friendly while driving, but…….
―
Electric vehicles are in a mad rush toward zero
carbon.
However, for some reason, a controversy has arisen that electric vehicles are greenwashing*. What could they mean by stating that EVs are damaging
the environment?
*Greenwashing: A compound word of
"green" and "whitewashing"; it refers to camouflage
environmentalism.
http://www.sunhakpeaceprize.org/kr/news/issue.php?bgu=view&idx=586
(Go to previous Sunhak Peace Prize article on Greenwashing)
Here we present the case that even electric
vehicles are actually greenwashing.
Over
the entire life cycle assessment (LCA) of EVs from production to disposal, more
carbon is emitted than internal combustion engine vehicles.
The heart of an electric
vehicle is the battery. It is argued that an inordinate amount of carbon is
emitted because electricity produced from fossil fuels is used in the
production and disposal of batteries.
※ CO2
emissions per km
According to the test results of the Korean
Ministry of Environment in 2016, the amount of carbon dioxide generated per
km was △86.9g for electric vehicles, △137g for diesel vehicles, and △177g for gasoline vehicles.
※ Carbon
dioxide emissions including production and disposal processes
However, when the production and disposal processes
are included, △electric vehicles weighed in at 49.12g △diesel vehicles 44.55g △gasoline vehicles 44.55g.
In Nov. 2019, German automaker Volkswagen conducted
a similar experiment.
The Volkswagen Group
announced a comparison of carbon dioxide emissions from
production to driving of its electric and diesel vehicles.
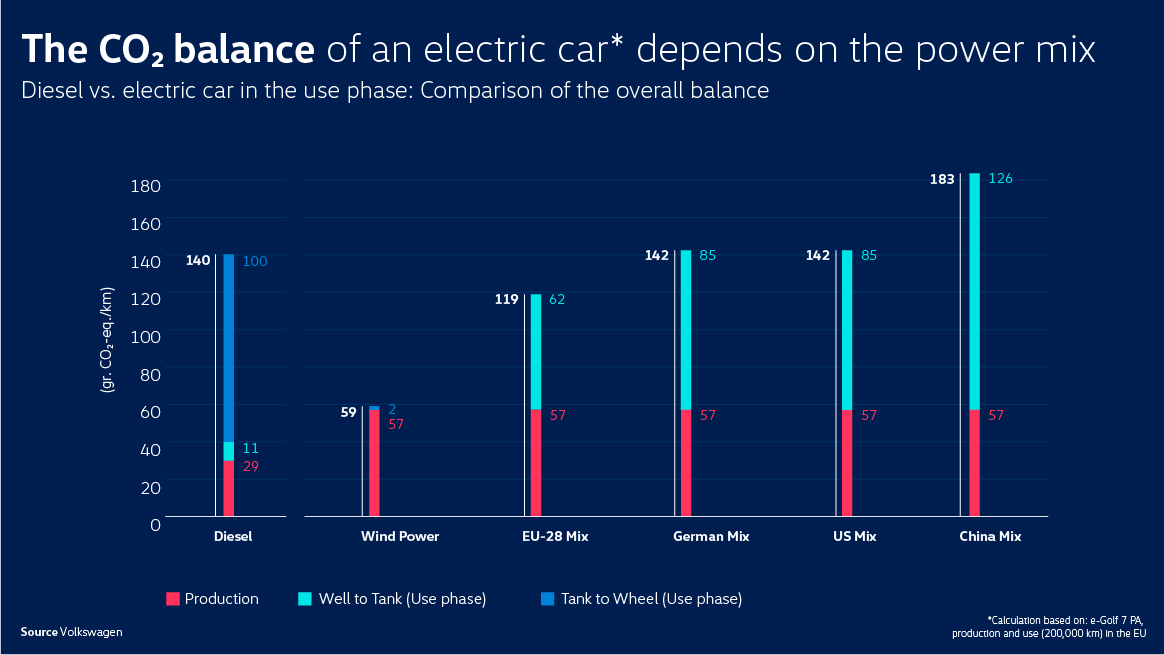
*Well to Tank : fuel production stage
*Tank to Wheel : fuel consumption stage
※ CO2
emissions per km
The amount of CO2 emissions per km was
△142 g for electric vehicles and △140 g for diesel vehicles, showing that EVs emit more carbon dioxide.
However, while driving, EVs produced zero carbon
dioxide emissions while driving, while diesel vehicles emitted 100
grams of carbon dioxide.
※ Carbon
dioxide emissions during vehicle production
On the other hand, during vehicle production,
△EVs emitted 57g of CO2 while △Diesel vehicles produced 29g of carbon dioxide.
※ Carbon
dioxide emissions during fuel production
Since, in the fuel production process △85g~126g for electric vehicles △11g for diesel vehicles, electric vehicles are shown to generate more carbon dioxide.
Both experiments in Korea and
Germany conclude that electric vehicles are eco-friendly in the driving
phase.
―
Batteries produce huge, amounts of carbon dioxide
―
※ Carbon
dioxide emission during the battery production stage
Rare
earth metals such as lithium and cobalt are contained in batteries, which are core components of electric vehicles. During
the mining and smelting of these minerals, harmful by-products and air
pollutants are generated. It is also noted that an enormous amount of
groundwater is required for mining.
Channel 4, a British private broadcaster, reported
on the poor mining site and damage situation in the Democratic Republic of
Congo in Africa on the current affairs program Unreported World, and the
scene was shocking.

(Cobalt mining site in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Source: Unreported
World)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ipOeH7GW0M8
70% of the world's cobalt is mined in Central
Africa, most of which comes from southern Katanga, one of the 10 most polluted
places on earth.
Young people in this country are mining cobalt, a
heavy metal, for 12 hours a day with bare hands without any protective
equipment to earn 150 dollars a month. It is said that even children
are driven to the mining site.

In addition, toxic substances from the mining
process flow into the river, killing fish, and many children with
disabilities are being born near the mine.
As a result, many global companies are joining the
Responsible Minerals Initiative (RMI), an international cooperative that
monitors whether the minerals required for battery production are ethically
produced and distributed.
In addition, the European Transport &
Environment Federation (Transport & Environment) predicts that the amount
of metal required for batteries will be reduced as the technology develops,
which will increase the eco-friendliness in the battery production stage.
We are also developing a technology using sodium, that can be extracted from
seawater, instead of lithium, which causes groundwater contamination during the
mining process.
―
Waste batteries are difficult to treat
―
※ Carbon
dioxide emissions when disposing of batteries
There is also a risk of environmental pollution at
the battery disposal stage of electric vehicles. Waste batteries are made of several heavy metals classified as toxic. Greenpeace forecasts that by 2030, global waste
battery emissions will reach about 12 million tons per year.
The reality is that most countries now store waste
batteries in separate facilities. Considering that the replacement cycle for
EV batteries is 5 to 10 years, disposal of waste batteries is also a matter of
time.
Fortunately, there is quite active discussion about
recycling waste batteries. Technology is being developed to utilize
waste batteries as an energy storage system (ESS) or to recycle decomposed
minerals.
SNE Research, a market research firm, predicts that
the global waste battery recycling market will grow to 600 trillion won by
2050.
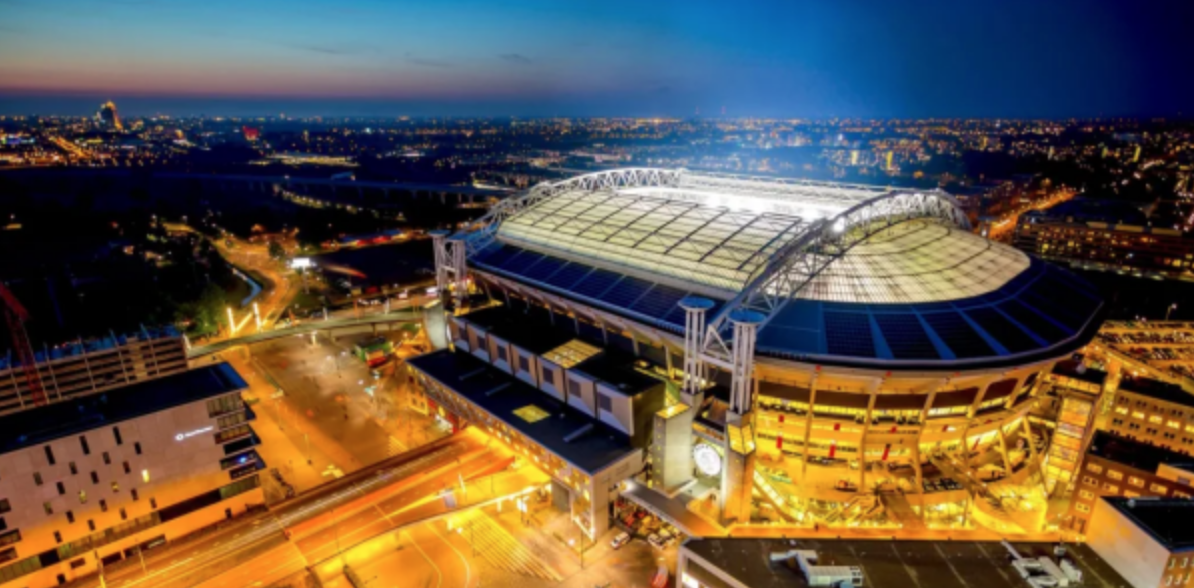

(Johan Cruyff soccer field in Holland uses electric vehicle batteries as
solar modules, Source: Electric)
German chemical company and recycling specialist
Duesenfeld announced that it has succeeded in recycling 96% by disassembling
lithium-ion batteries, extracting raw materials such as nickel, manganese,
cobalt, and lithium, and refurbishing them for battery operation.
―
Electric vehicles powered by renewable energy
―
The production of electricity, the power
source for electric vehicles, from fossil fuels such as coal and oil, is
also a hurdle to overcome.
As an alternative, research is underway for using
renewable forms including solar as energy sources to generate electricity.
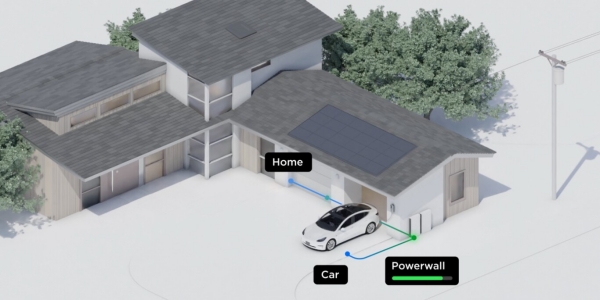
(image source, Tesla)
Tesla, a global leader in electric vehicles, has commercialized
home energy storage devices using solar power.
Tesla advertises
charging its vehicles through an energy storage device called a “power wall”
which can also service household electricity.
Volkswagen Group predicts that once renewable
energy sources such as solar and wind are used to power electric vehicles, CO2
emissions will drop dramatically from 62g per kilometer to 2g per kilometer
based on the EU electric mix.
―
What we can do for green transport
―
In fact, the carbon
emission of electric vehicles differs according to the research method of each
country and institution. According to Life
Cycle Assessment (LCA), there are reports that EVs emit less CO2
than fossil fueled vehicles.

Citing a report titled “The Underestimated
Potential of Battery Electric Vehicles to Reduce Emissions,” published in
the Dutch Scientific Journal in 2019, it states that electric
vehicles are more environmentally friendly.
It points out that the
greenwashing controversy over EVs arises due to △ overestimation of the amount of carbon dioxide generated during battery
manufacturing △underestimation of battery life △assumption that the power source will still be
based on fossil fuels △unrealistic application of energy consumption measurement method.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2542435119302715
International Council
for Clean Transport (ICCT), a non-profit
organization, likewise reports that electric vehicles emit less greenhouse
gas than internal combustion
automobiles, regardless of what fuel they are supplied with.
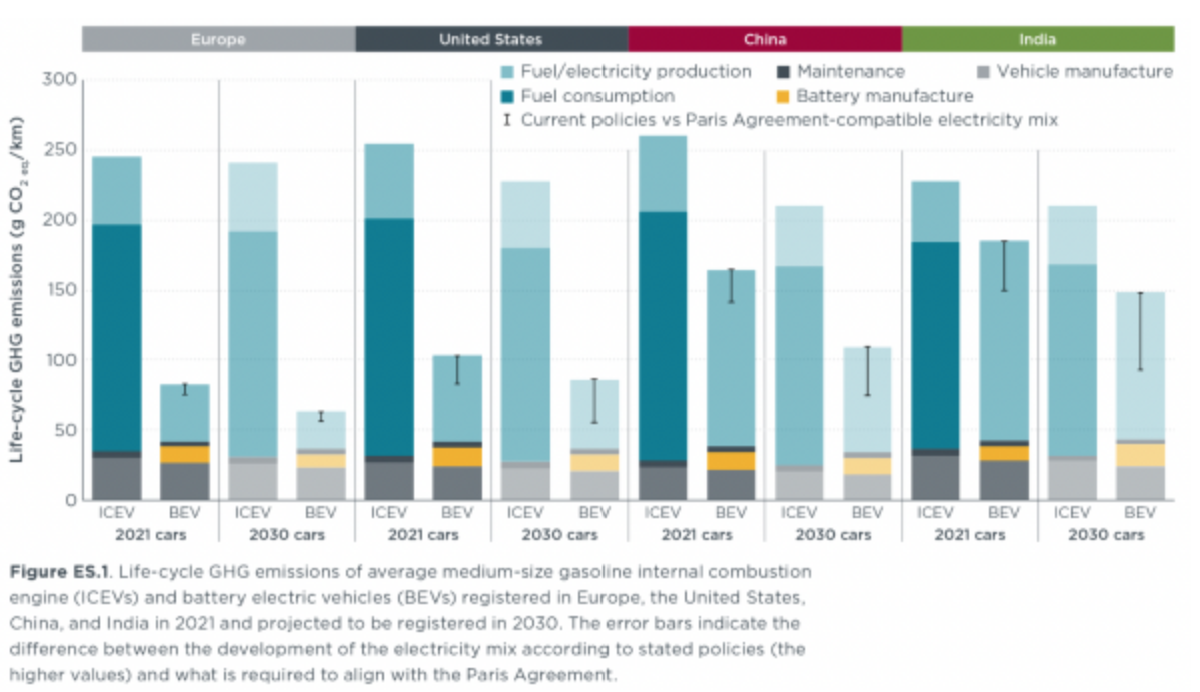
(Comparison of greenhouse gas emissions throughout the life cycle of internal combustion engine vehicles (ICEVs) and electric vehicles (BEVs) by country)
The UN Member States’ goal to achieve net zero
by 2050 is a global promise. To achieve this goal, zero-emission
vehicles should account for 61% of global new car sales by 2030 and 93% by
2035. But it doesn't seem easy.
It is clear that technological development will help reduce carbon. But one of the quickest and surest ways we can practice it is to reduce the use of cars by walking, biking and using more eco-friendly public transport.
Written by Sharon Choi
Director of Planning
Sunhak Peace Prize Secretariat

